Can exosomes deliver targeted treatments
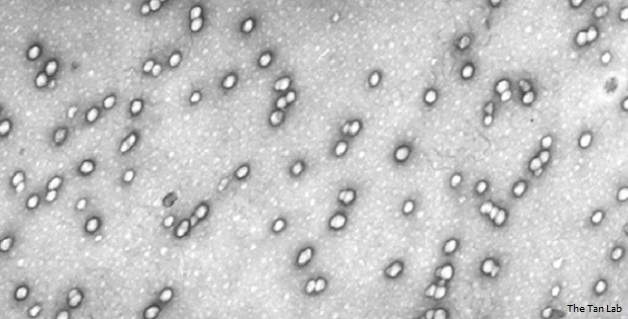
Exosomes are small membrane vesicles that are released and internalised by cells. Exosomes are found in almost all biological fluids including the blood and urine. Exosomes have a diameter between 30 and 150 nM whilst red blood cells in comparison are approximately 6000 – 8000 nM. Among many proposed functions, exosomes play an important role in waste management / metabolism and cell signaling. Exosomes contain protein, RNA and a range of other biochemicals depending on the cell / tissue of origin. As they circulate around the body exosomes can travel relatively large distances before delivering their 'cargo'.
There is a growing interest in exosomes due to their potential prognostic / biomarker value as well as their possible therapeutic potential. New company Codiak BioSciences has a mission to assess the role exosomes may be able to play in fighting cancer and a range of other diseases. Codiak BioSciences has received approximately 80 million dollars US for its initial round of funding. It is hoped that exosomes may be used as drug delivery vehicles to target specific cancer cells. Beyond drugs, exosomes may also be able to play a role in delivering RNA silencing based therapies in a targeted manner. The options are vast. This may only be the beginning, but clearly exosome research has a big future.